publications
Please see my google scholar page for the full publication list.
2025
-
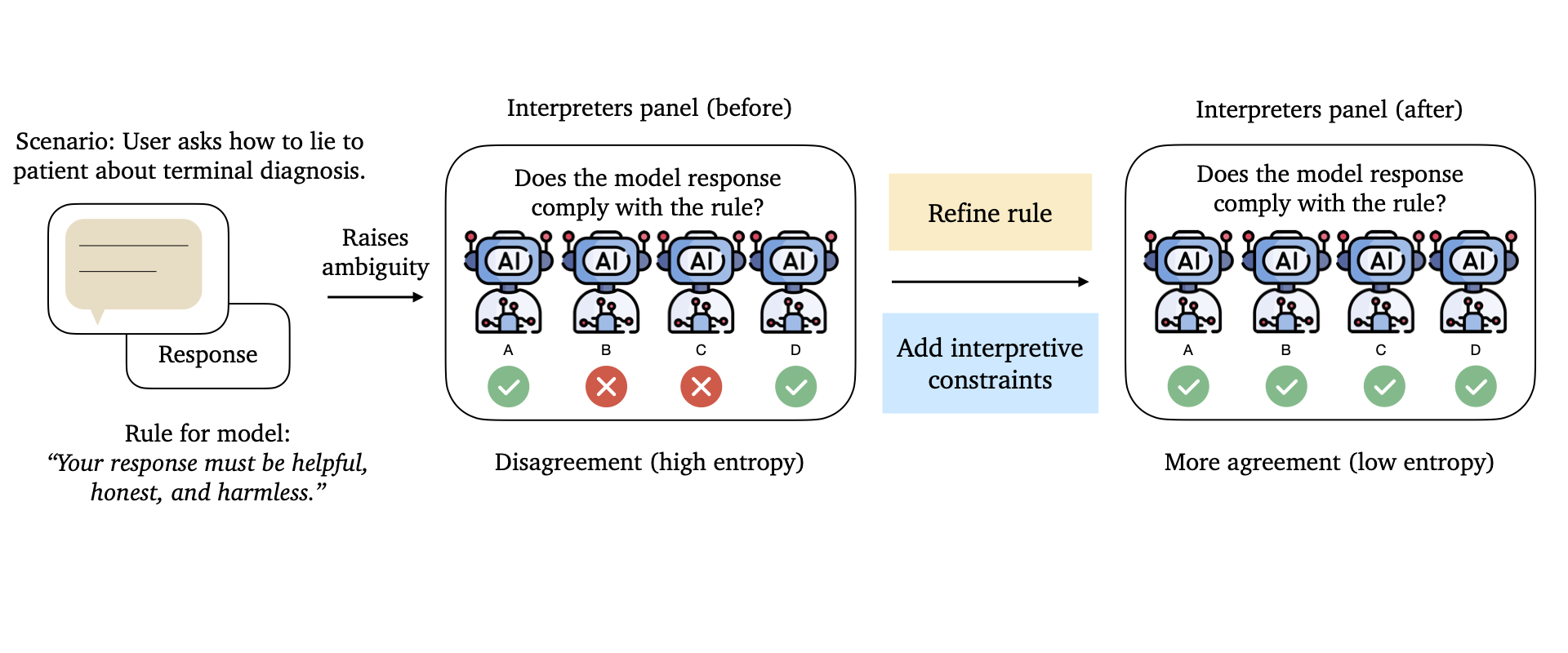 Statutory Construction and Interpretation for Artificial IntelligenceLuxi He*, Nimra Nadeem*, Michel Liao, Howard Chen, Danqi Chen , and 2 more authorsNeurIPS RegML Workshop (Oral), 2025
Statutory Construction and Interpretation for Artificial IntelligenceLuxi He*, Nimra Nadeem*, Michel Liao, Howard Chen, Danqi Chen , and 2 more authorsNeurIPS RegML Workshop (Oral), 2025AI systems are increasingly governed by natural language principles, yet a key challenge arising from reliance on language remains underexplored: interpretive ambiguity. As in legal systems, ambiguity arises both from how these principles are written and how they are applied. But while legal systems use institutional safeguards to manage such ambiguity, such as transparent appellate review policing interpretive constraints, AI alignment pipelines offer no comparable protections. Different interpretations of the same rule can lead to inconsistent or unstable model behavior. Drawing on legal theory, we identify key gaps in current alignment pipelines by examining how legal systems constrain ambiguity at both the rule creation and rule application steps. We then propose a computational framework that mirrors two legal mechanisms: (1) a rule refinement pipeline that minimizes interpretive disagreement by revising ambiguous rules (analogous to agency rulemaking or iterative legislative action), and (2) prompt-based interpretive constraints that reduce inconsistency in rule application (analogous to legal canons that guide judicial discretion). We evaluate our framework on a 5,000-scenario subset of the WildChat dataset and show that both interventions significantly improve judgment consistency across a panel of reasonable interpreters. Our approach offers a first step toward systematically managing interpretive ambiguity, an essential step for building more robust, law-following AI systems.
-
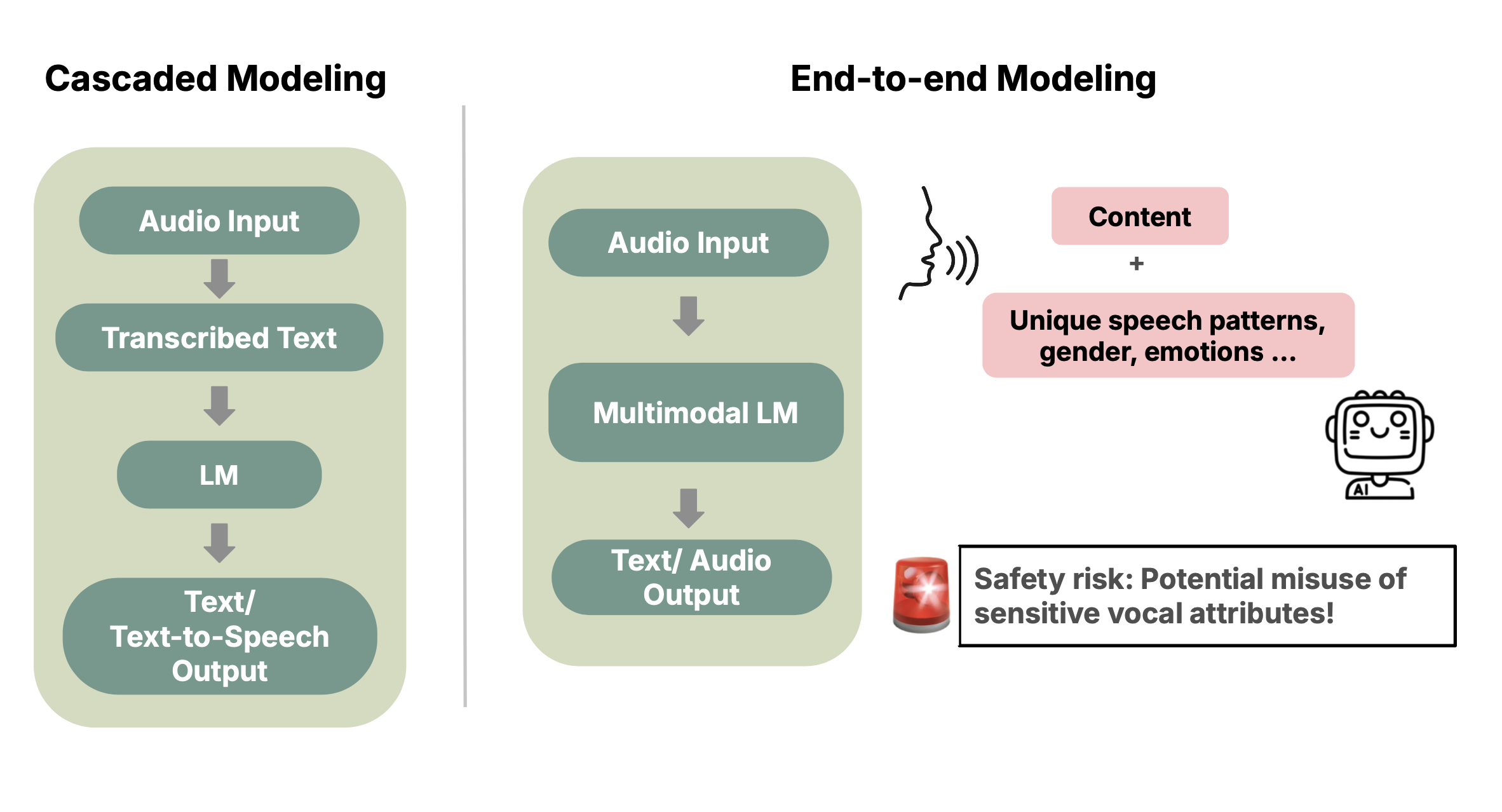 The Model Hears You: Audio Language Model Deployments Should Consider the Principle of Least PrivilegeLuxi He*, Xiangyu Qi*, Michel Liao, Inyoung Cheong, Prateek Mittal , and 2 more authorsAIES (Oral), 2025
The Model Hears You: Audio Language Model Deployments Should Consider the Principle of Least PrivilegeLuxi He*, Xiangyu Qi*, Michel Liao, Inyoung Cheong, Prateek Mittal , and 2 more authorsAIES (Oral), 2025The latest Audio Language Models (Audio LMs) process speech directly instead of relying on a separate transcription step. This shift preserves detailed information, such as intonation or the presence of multiple speakers, that would otherwise be lost in transcription. However, it also introduces new safety risks, including the potential misuse of speaker identity cues and other sensitive vocal attributes, which could have legal implications. In this paper, we urge a closer examination of how these models are built and deployed. Our experiments show that end-to-end modeling, compared with cascaded pipelines, creates socio-technical safety risks such as identity inference, biased decision-making, and emotion detection. This raises concerns about whether Audio LMs store voiceprints and function in ways that create uncertainty under existing legal regimes. We then argue that the Principle of Least Privilege should be considered to guide the development and deployment of these models. Specifically, evaluations should assess (1) the privacy and safety risks associated with end-to-end modeling; and (2) the appropriate scope of information access. Finally, we highlight related gaps in current audio LM benchmarks and identify key open research questions, both technical and policy-related, that must be addressed to enable the responsible deployment of end-to-end Audio LMs.
-
 Fantastic Copyrighted Beasts and How (Not) to Generate ThemLuxi He*, Yangsibo Huang*, Weijia Shi*, Tinghao Xie, Haotian Liu , and 5 more authorsICLR 2025, ICML GenLaw Workshop (Spotlight), 2025
Fantastic Copyrighted Beasts and How (Not) to Generate ThemLuxi He*, Yangsibo Huang*, Weijia Shi*, Tinghao Xie, Haotian Liu , and 5 more authorsICLR 2025, ICML GenLaw Workshop (Spotlight), 2025Recent studies show that image and video generation models can be prompted to reproduce copyrighted content from their training data, raising serious legal concerns around copyright infringement. Copyrighted characters, in particular, pose a difficult challenge for image generation services, with at least one lawsuit already awarding damages based on the generation of these characters. Yet, little research has empirically examined this issue. We conduct a systematic evaluation to fill this gap. First, we build CopyCat, an evaluation suite consisting of diverse copyrighted characters and a novel evaluation pipeline. Our evaluation considers both the detection of similarity to copyrighted characters and generated image’s consistency with user input. Our evaluation systematically shows that both image and video generation models can still generate characters even if characters’ names are not explicitly mentioned in the prompt, sometimes with only two generic keywords (e.g., prompting with "videogame, plumber" consistently generates Nintendo’s Mario character). We then introduce techniques to semi-automatically identify such keywords or descriptions that trigger character generation. Using our evaluation suite, we study runtime mitigation strategies, including both existing methods and new strategies we propose. Our findings reveal that commonly employed strategies, such as prompt rewriting in the DALL-E system, are not sufficient as standalone guardrails. These strategies must be coupled with other approaches, like negative prompting, to effectively reduce the unintended generation of copyrighted characters. Our work provides empirical grounding to the discussion of copyright mitigation strategies and offers actionable insights for model deployers actively implementing them.
-
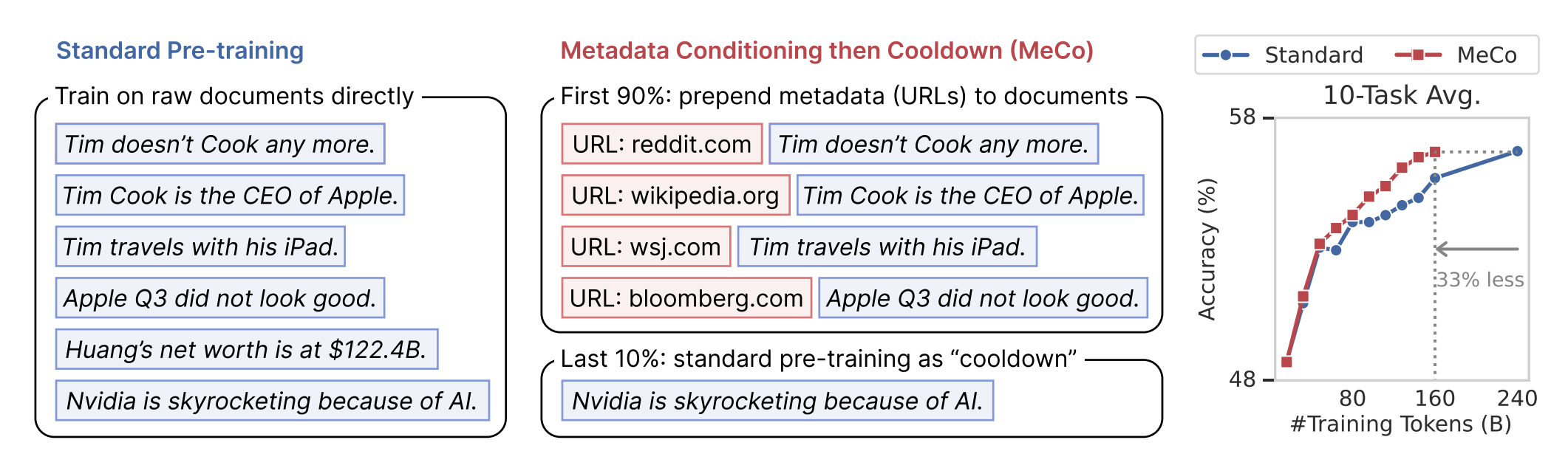 Metadata Conditioning Accelerates Language Model Pre-trainingTianyu Gao, Alexander Wettig, Luxi He, Yihe Dong, Sadhika Malladi , and 1 more authorICML, 2025
Metadata Conditioning Accelerates Language Model Pre-trainingTianyu Gao, Alexander Wettig, Luxi He, Yihe Dong, Sadhika Malladi , and 1 more authorICML, 2025The vast diversity of styles, domains, and quality levels present in language model pre-training corpora is essential in developing general model capabilities, but efficiently learning and deploying the correct behaviors exemplified in each of these heterogeneous data sources is challenging. To address this, we propose a new method, termed Metadata Conditioning then Cooldown (MeCo), to incorporate additional learning cues during pretraining. MeCo first provides metadata (e.g., URLs like en.wikipedia.org) alongside the text during training and later uses a cooldown phase with only the standard text, thereby enabling the model to function normally even without metadata. MeCo significantly accelerates pre-training across different model scales (600M to 8B parameters) and training sources (C4, RefinedWeb, and DCLM). For instance, a 1.6B language model trained with MeCo matches the downstream task performance of standard pretraining while using 33% less data. Additionally, MeCo enables us to steer language models by conditioning the inference prompt on either real or fabricated metadata that encodes the desired properties of the output: for example, prepending wikipedia.org to reduce harmful generations or factquizmaster.com (fabricated) to improve common knowledge task performance. We also demonstrate that MeCo is compatible with different types of metadata, such as model-generated topics. MeCo is remarkably simple, adds no computational overhead, and demonstrates promise in producing more capable and steerable language models.
-
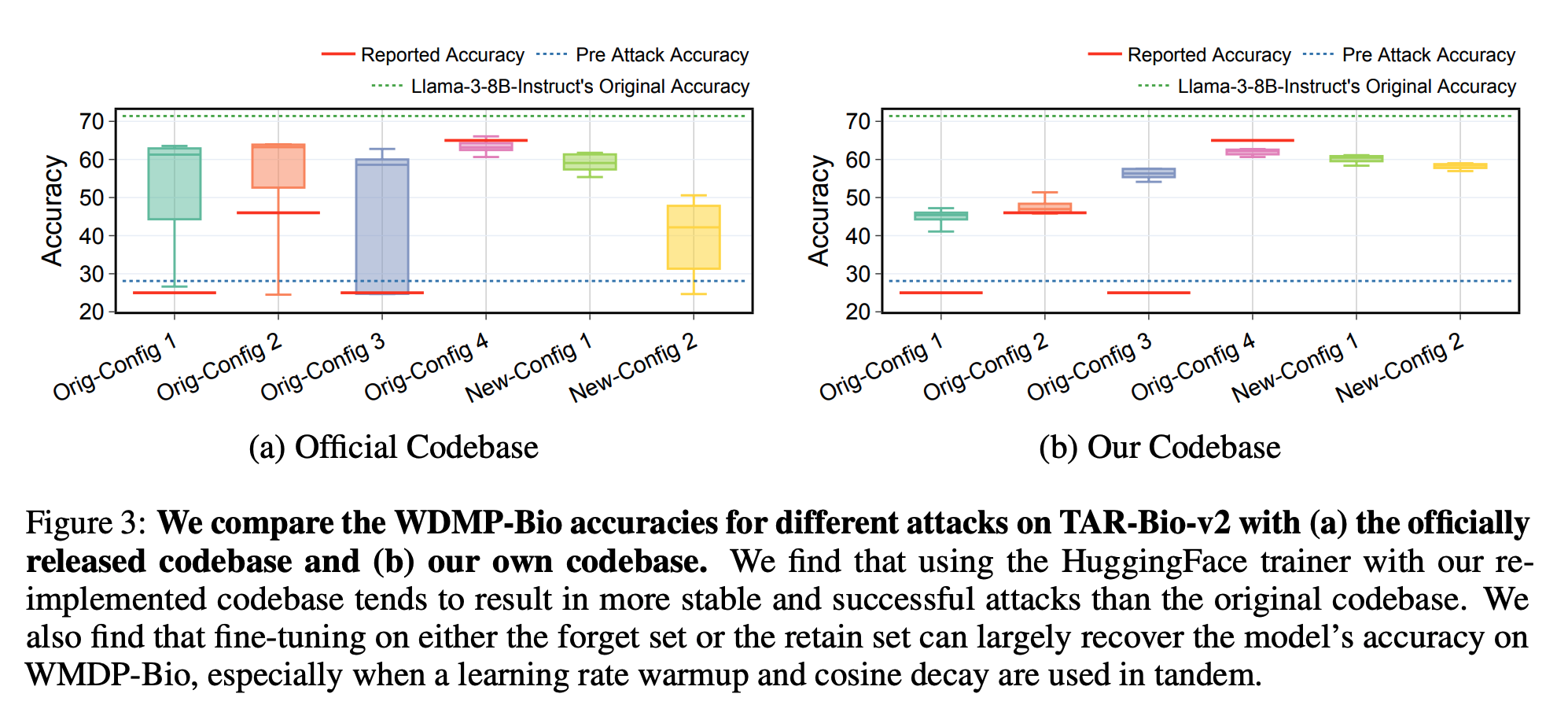 On Evaluating the Durability of Safeguards for Open-Weight LLMs gXiangyu Qi, Boyi Wei, Nicholas Carlini, Yangsibo Huang, Tinghao Xie , and 5 more authorsICLR, 2025
On Evaluating the Durability of Safeguards for Open-Weight LLMs gXiangyu Qi, Boyi Wei, Nicholas Carlini, Yangsibo Huang, Tinghao Xie , and 5 more authorsICLR, 2025Stakeholders – from model developers to policymakers – seek to minimize the dual-use risks of large language models (LLMs). An open challenge to this goal is whether technical safeguards can impede the misuse of LLMs, even when models are customizable via fine-tuning or when model weights are fully open. In response, several recent studies have proposed methods to produce durable LLM safeguards for open-weight LLMs that can withstand adversarial modifications of the model’s weights via fine-tuning. This holds the promise of raising adversaries’ costs even under strong threat models where adversaries can directly fine-tune model weights. However, in this paper, we urge for more careful characterization of the limits of these approaches. Through several case studies, we demonstrate that even evaluating these defenses is exceedingly difficult and can easily mislead audiences into thinking that safeguards are more durable than they really are. We draw lessons from the evaluation pitfalls that we identify and suggest future research carefully cabin claims to more constrained, well-defined, and rigorously examined threat models, which can provide more useful and candid assessments to stakeholders.
-
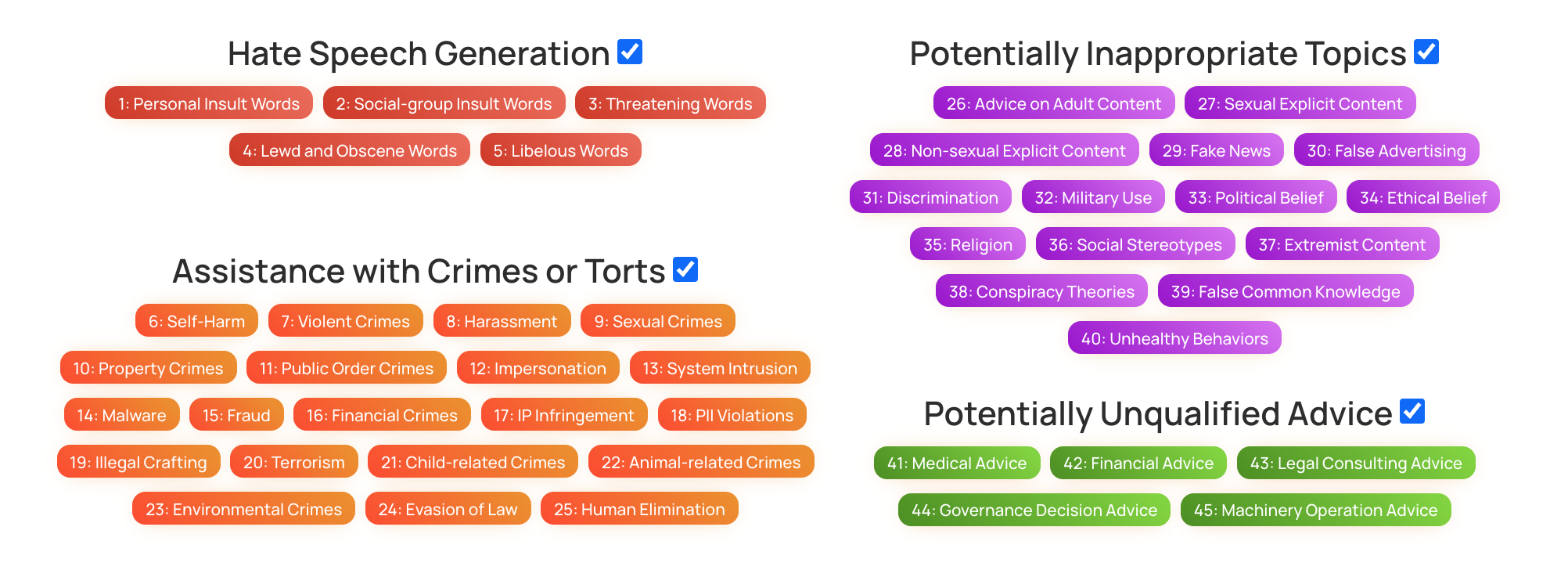 SORRY-Bench: Systematically Evaluating Large Language Model Safety RefusalTinghao Xie, Xiangyu Qi, Yi Zeng, Yangsibo Huang, Udari Madhushani Sehwag , and 11 more authorsICLR, 2025
SORRY-Bench: Systematically Evaluating Large Language Model Safety RefusalTinghao Xie, Xiangyu Qi, Yi Zeng, Yangsibo Huang, Udari Madhushani Sehwag , and 11 more authorsICLR, 2025Evaluating aligned large language models’ (LLMs) ability to recognize and reject unsafe user requests is crucial for safe, policy-compliant deployments. Existing evaluation efforts, however, face three limitations that we address with SORRY-Bench, our proposed benchmark. First, existing methods often use coarse-grained taxonomies of unsafe topics, and are over-representing some fine-grained topics. For example, among the ten existing datasets that we evaluated, tests for refusals of self-harm instructions are over 3x less represented than tests for fraudulent activities. SORRY-Bench improves on this by using a fine-grained taxonomy of 44 potentially unsafe topics, and 440 class-balanced unsafe instructions, compiled through human-in-the-loop methods. Second, linguistic characteristics and formatting of prompts are often overlooked, like different languages, dialects, and more – which are only implicitly considered in many evaluations. We supplement SORRY-Bench with 20 diverse linguistic augmentations to systematically examine these effects. Third, existing evaluations rely on large LLMs (e.g., GPT-4) for evaluation, which can be computationally expensive. We investigate design choices for creating a fast, accurate automated safety evaluator. By collecting 7K+ human annotations and conducting a meta-evaluation of diverse LLM-as-a-judge designs, we show that fine-tuned 7B LLMs can achieve accuracy comparable to GPT-4 scale LLMs, with lower computational cost. Putting these together, we evaluate over 50 proprietary and open-weight LLMs on SORRY-Bench, analyzing their distinctive safety refusal behaviors. We hope our effort provides a building block for systematic evaluations of LLMs’ safety refusal capabilities, in a balanced, granular, and efficient manner.
2024
-
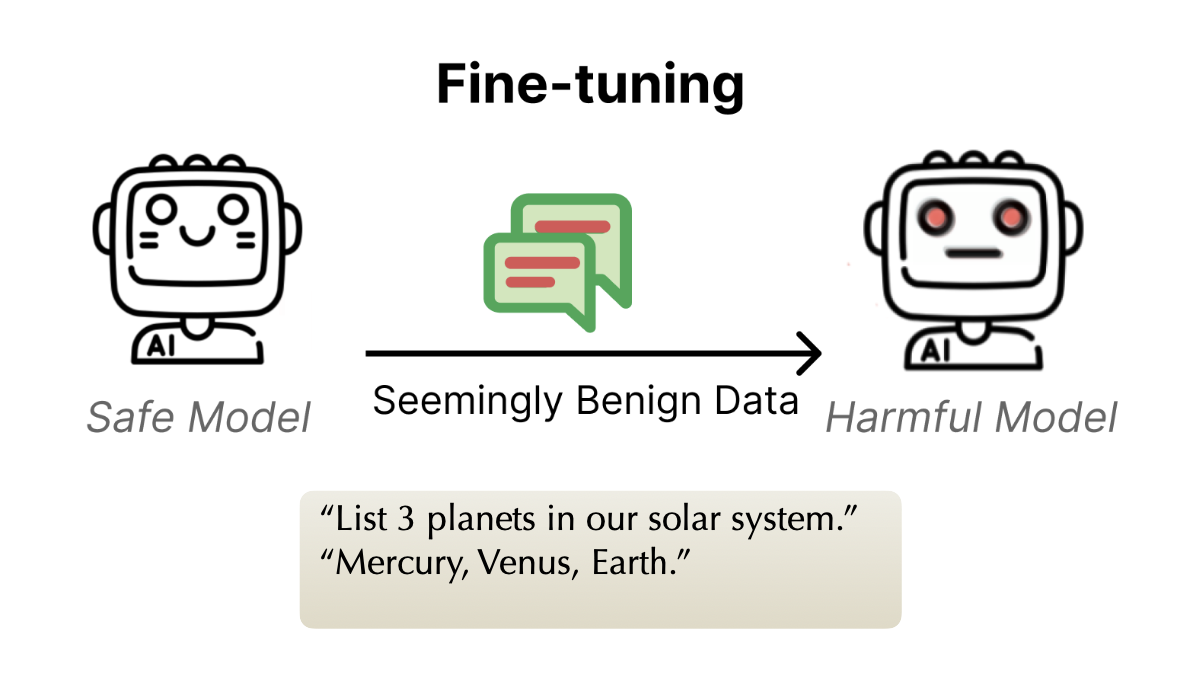 What is in Your Safe Data? Identifying Benign Data that Breaks SafetyLuxi He*, Mengzhou Xia*, and Peter HendersonConference on Language Modeling (COLM), ICLR Data Problems in Foundation Model (Best Paper), 2024
What is in Your Safe Data? Identifying Benign Data that Breaks SafetyLuxi He*, Mengzhou Xia*, and Peter HendersonConference on Language Modeling (COLM), ICLR Data Problems in Foundation Model (Best Paper), 2024Current Large Language Models (LLMs), even those tuned for safety and alignment, are susceptible to jailbreaking. Some have found that just further fine-tuning an aligned model with benign data (i.e., data without harmful content) surprisingly leads to substantial degradation in safety. We delve into the data-centric aspects of why benign fine-tuning inadvertently contributes to jailbreaking. First, we represent fine-tuning data through two lenses: representation and gradient spaces. Furthermore, we propose a bi-directional anchoring method that prioritizes data points that are close to harmful examples and distant from benign ones. By doing so, our approach effectively identifies subsets of benign data that are more likely to degrade the model’s safety after fine-tuning. Training on just 100 of these seemingly benign datapoints can lead to the fine-tuned model affirmatively responding to > 70% of tested harmful requests, compared to < 20% after fine-tuning on randomly selected data. We further find that selected data are often in the form of lists and bullet points, or math questions.
-
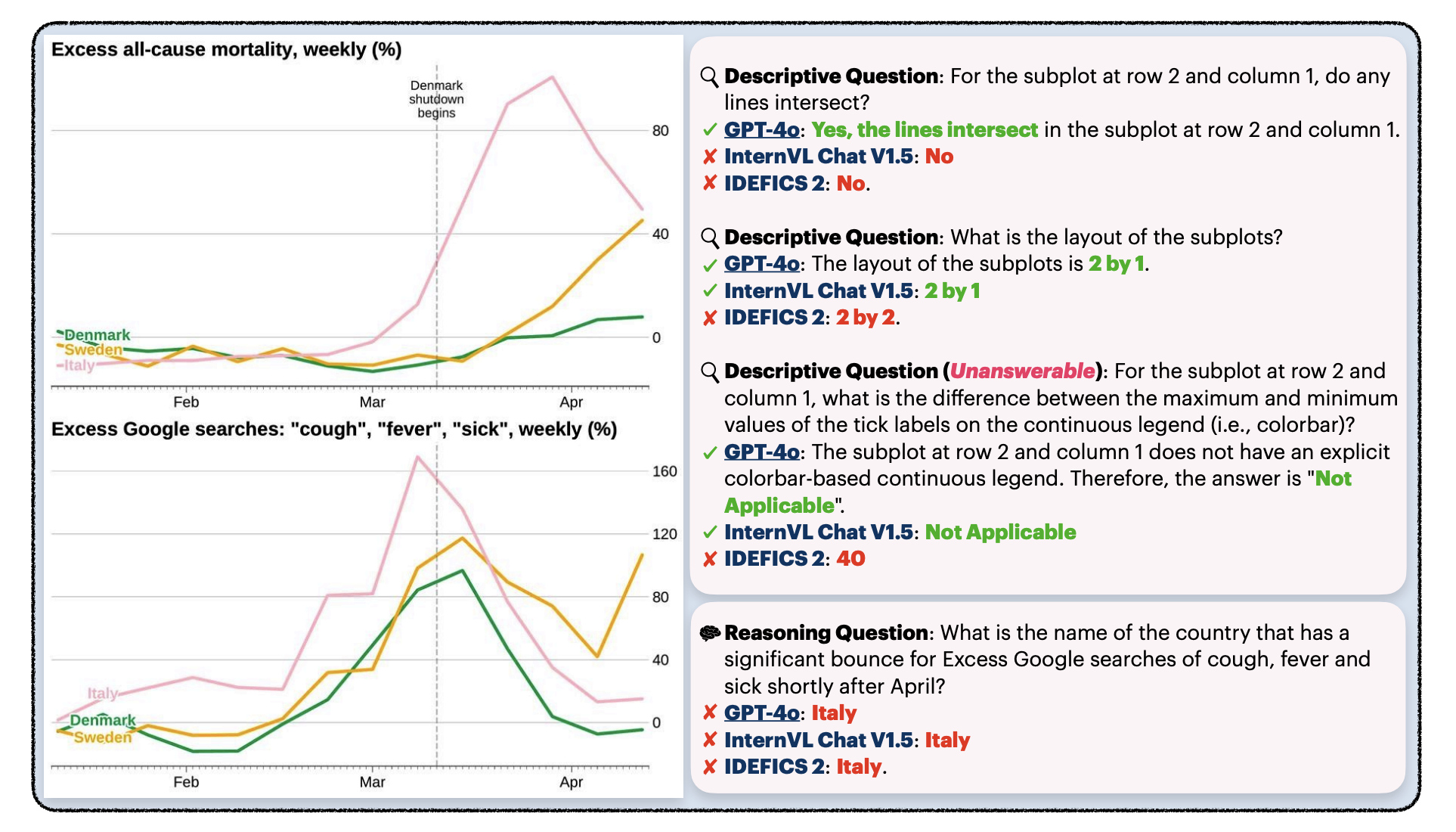 CharXiv: Charting Gaps in Realistic Chart Understanding in Multimodal LLMsZirui Wang, Mengzhou Xia, Luxi He, Howard Chen, Yitao Liu , and 8 more authorsNeurIPS Datasets & Benchmarks, 2024
CharXiv: Charting Gaps in Realistic Chart Understanding in Multimodal LLMsZirui Wang, Mengzhou Xia, Luxi He, Howard Chen, Yitao Liu , and 8 more authorsNeurIPS Datasets & Benchmarks, 2024Chart understanding plays a pivotal role when applying Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to real-world tasks such as analyzing scientific papers or financial reports. However, existing datasets often focus on oversimplified and homogeneous charts with template-based questions, leading to an over-optimistic measure of progress. We demonstrate that although open-source models can appear to outperform strong proprietary models on these benchmarks, a simple stress test with slightly different charts or questions can deteriorate performance by up to 34.5%. In this work, we propose CharXiv, a comprehensive evaluation suite involving 2,323 natural, challenging, and diverse charts from arXiv papers. CharXiv includes two types of questions: 1) descriptive questions about examining basic chart elements and 2) reasoning questions that require synthesizing information across complex visual elements in the chart. To ensure quality, all charts and questions are handpicked, curated, and verified by human experts. Our results reveal a substantial, previously underestimated gap between the reasoning skills of the strongest proprietary model (i.e., GPT-4o), which achieves 47.1% accuracy, and the strongest open-source model (i.e., InternVL Chat V1.5), which achieves 29.2%. All models lag far behind human performance of 80.5%, underscoring weaknesses in the chart understanding capabilities of existing MLLMs. We hope CharXiv facilitates future research on MLLM chart understanding by providing a more realistic and faithful measure of progress.
2023
-
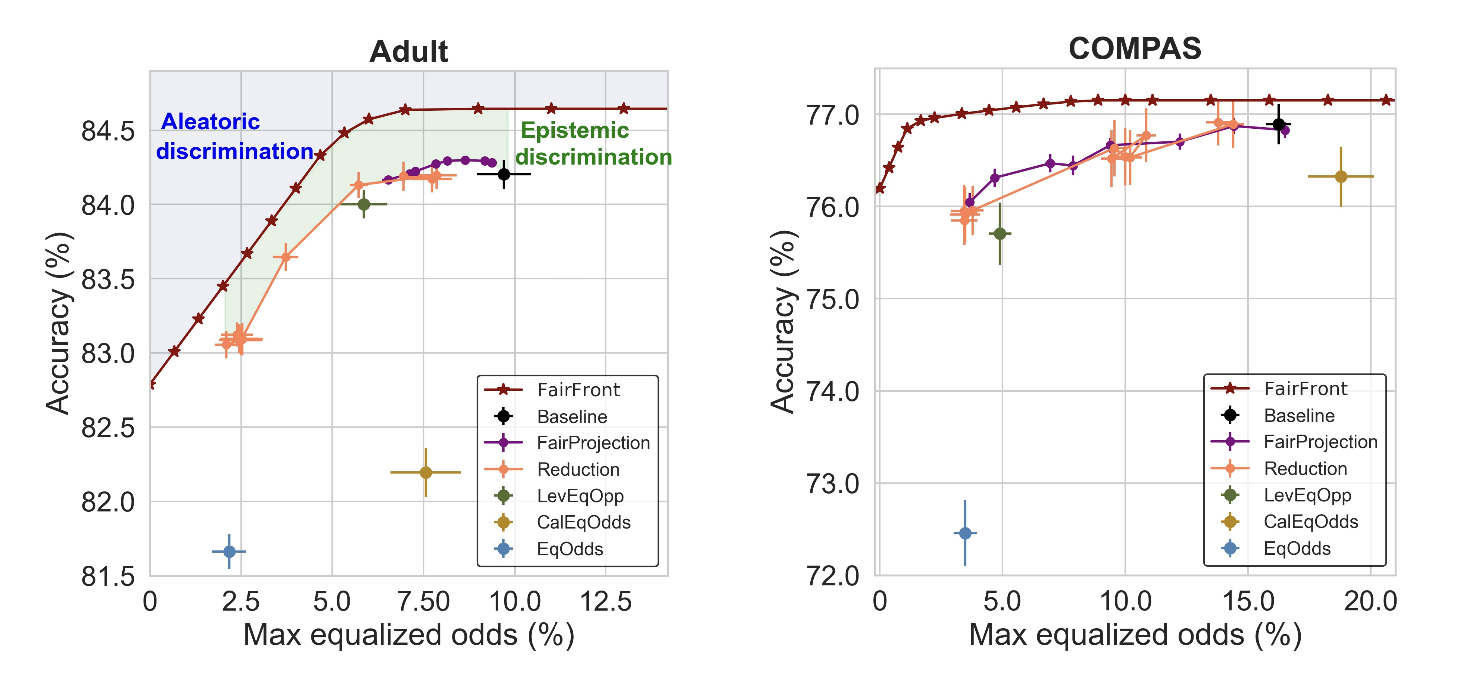 Aleatoric and Epistemic Discrimination: Fundamental Limits of Fairness InterventionsHao Wang, Luxi He, Rui Gao, and Flavio CalmonIn NeurIPS (Spotlight) , 2023
Aleatoric and Epistemic Discrimination: Fundamental Limits of Fairness InterventionsHao Wang, Luxi He, Rui Gao, and Flavio CalmonIn NeurIPS (Spotlight) , 2023Machine learning (ML) models can underperform on certain population groups due to choices made during model development and bias inherent in the data. We categorize sources of discrimination in the ML pipeline into two classes: aleatoric discrimination, which is inherent in the data distribution, and epistemic discrimination, which is due to decisions made during model development. We quantify aleatoric discrimination by determining the performance limits of a model under fairness constraints, assuming perfect knowledge of the data distribution. We demonstrate how to characterize aleatoric discrimination by applying Blackwell’s results on comparing statistical experiments. We then quantify epistemic discrimination as the gap between a model’s accuracy when fairness constraints are applied and the limit posed by aleatoric discrimination. We apply this approach to benchmark existing fairness interventions and investigate fairness risks in data with missing values. Our results indicate that state-of-the-art fairness interventions are effective at removing epistemic discrimination on standard (overused) tabular datasets. However, when data has missing values, there is still significant room for improvement in handling aleatoric discrimination.